9.5: Chapter 9 Exercises
- Page ID
- 27818
For exercises 1-6, show all 5 steps for hypothesis testing:
a) State the hypotheses.
b) Compute the test statistic.
c) Compute the critical value or p-value.
d) State the decision.
e) Write a summary.
1. An adviser is testing out a new online learning module for a placement test. Test the claim that on average the new online learning module increased placement scores at a significance level of \(\alpha\) = 0.05. For the context of this problem, μD=μBefore–μAfter where the first data set represents the after test scores and the second data set represents before test scores. Assume the population is normally distributed. You obtain the following paired sample of 19 students that took the placement test before and after the learning module.
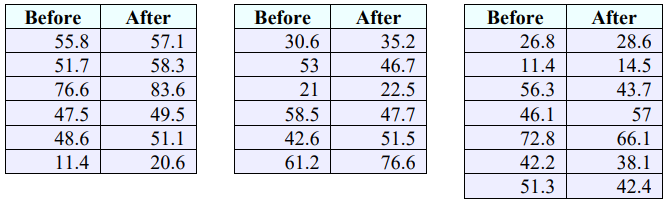
2. A veterinary nutritionist developed a diet for overweight dogs. The total volume of food consumed remains the same, but half of the dog food is replaced with a low-calorie “filler” such as green beans. Ten overweight dogs were randomly selected from her practice and were put on this program. Their initial weights were recorded, and then the same dogs were weighed again after 4 weeks. At the 0.01 level of significance, can it be concluded that the dogs lost weight? Use the following computer output to answer the following questions. Assume the populations are normally distributed and the groups are dependent.
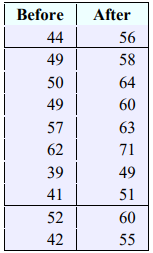
3. A manager wishes to see if the time (in minutes) it takes for their workers to complete a certain task will decrease when they are allowed to wear earbuds at work. A random sample of 20 workers' times was collected before and after. Test the claim that the time to complete the task has decreased at a significance level of \(\alpha\) = 0.01. For the context of this problem, μD=μBefore–μAfter where the first data set represents before measurement and the second data set represents the after measurement. Assume the population is normally distributed. You obtain the following sample data.
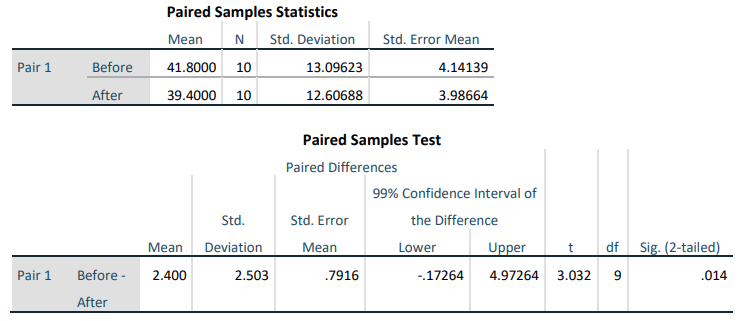
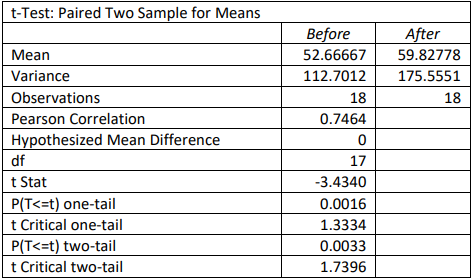
4. A physician wants to see if there was a difference in the average smoker’s daily cigarette consumption after wearing a nicotine patch. The physician sets up a study to track daily smoking consumption. They give the patients a placebo patch that did not contain nicotine for 4 weeks, then a nicotine patch for the following 4 weeks. Use the following computer output to test to see if there was a difference in the average smoker’s daily cigarette consumption using \(\alpha\) = 0.01.
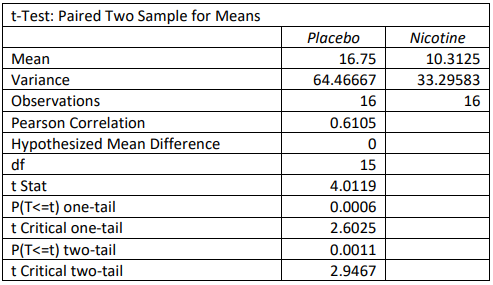
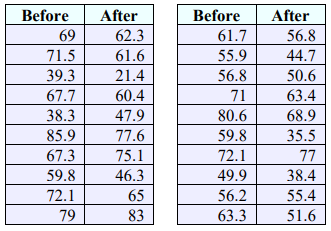
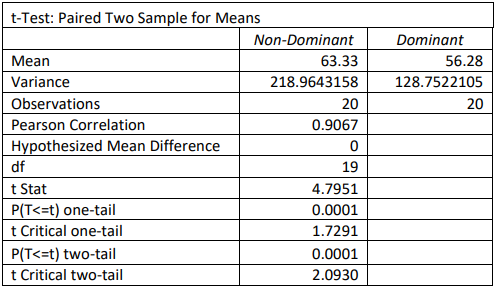
5. A researcher is testing reaction times between the dominant and non-dominant hand. They randomly start with different hands for 20 subjects and their reaction times for both hands is recorded in milliseconds. Use the following computer output to test to see if the reaction time is faster for the dominant hand using a 5% level of significance.
6. A manager wants to see if it is worth going back for an MBA degree. They randomly sample 18 managers' salaries before and after undertaking an MBA degree and record their salaries in thousands of dollars. Assume salaries are normally distributed. Use the following computer output to test the claim that the MBA degree, on average, increases a manager’s salary. Use a 10% level of significance.
7. Doctors developed an intensive intervention program for obese patients with heart disease. Subjects with a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or more with heart disease were assigned to a three-month lifestyle change of diet and exercise. Patients’ Left Ventricle Ejection Fraction (LVEF) are measured before and after intervention. Assume that LVEF measurements are normally distributed.
a) Find the 95% confidence interval for the mean of the differences.
b) Using the confidence interval answer, did the intensive intervention program significantly increase the mean LVEF? Explain why.
For exercises 8-14, show all 5 steps for hypothesis testing:
a) State the hypotheses.
b) Compute the test statistic.
c) Compute the critical value or p-value.
d) State the decision.
e) Write a summary.
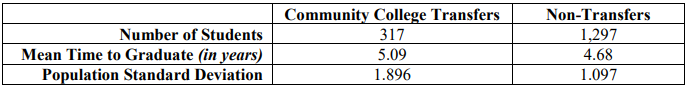
8. In a study that followed a group of students who graduated from high school in 1997, each was monitored in progress made toward earning a bachelor’s degree. The group was divided in two – those who started at community college and later transferred to a four-year college, and those that started out in a four-year college as freshmen. That data below summarizes the findings. Is there evidence to suggest that community college transfer students take longer to earn a bachelor’s degree? Use \(\alpha\) = 0.05.
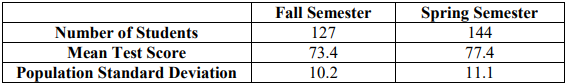
9. A liberal arts college in New Hampshire implemented an online homework system for their introductory math courses and wanted to know whether the system improved test scores. In the Fall semester, homework was completed with pencil and paper, checking answers in the back of the book. In the Spring semester, homework was completed online – giving students instant feedback on their work. The results are summarized below. Population standard deviations were used from past studies. Is there evidence to suggest that the online system improves test scores? Use \(\alpha\) = 0.05.
10. Researchers conducted a study to measure the effectiveness of the drug Adderall on patients diagnosed with ADHD. A total of 112 patients with ADHD were randomly split into two groups. Group 1 included 56 patients and they were each given a dose of 15 mg. of Adderall daily. The 56 patients in Group 2 were given a daily placebo. The effectiveness of the drug was measured by testing the patients score on a behavioral test. Higher scores indicate more ADHD symptoms. Group 1 was found to have a mean improvement of 9.3 points and Group 2 had a mean improvement of 11.7 points. From past studies, the population standard deviation of both groups is known to be 6.5 points. Is there evidence to suggest the patients taking Adderall have improved the mean ADHD symptoms? Test at the 0.01 level of significance.
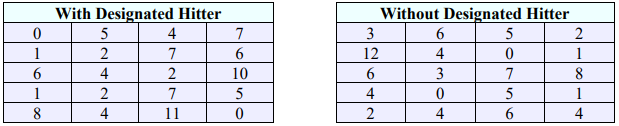
11. In Major League Baseball, the American League (AL) allows a designated hitter (DH) to bat in place of the pitcher, but in the National League (NL), the pitcher has to bat. However, when an AL team is the visiting team for a game against an NL team, the AL team must abide by the home team’s rules and thus, the pitcher must bat. A researcher is curious if an AL team would score more runs for games in which the DH was used. She samples 20 games for an AL team for which the DH was used, and 20 games for which there was no DH. The data are below. Assume the population is normally distributed with a population standard deviation for runs scored of 2.54. Is there evidence to suggest that AL team would score more runs for games in which the DH was used? Use \(\alpha\) = 0.10.
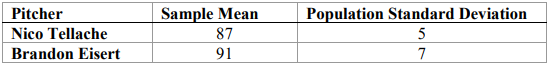
12. The mean speeds (mph) of fastball pitches from two different left-handed baseball pitchers are to be compared. A sample of 14 fastball pitches is measured from each pitcher. The populations have normal distributions. Scouts believe that Brandon Eisert pitches a speedier fastball. Test the scouts’ claim that Eisert’s mean speed is faster at the 5% level of significance?
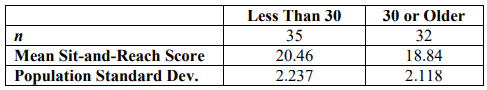
13. A physical therapist believes that at 30 years old adults begin to decline in flexibility and agility. To test this, they randomly sample 35 of their patients who are less than 30 years old and 32 of their patients who are 30 or older and measure each patient’s flexibility in the Sit-and-Reach test. The results are below. Is there evidence to suggest that adults under the age of 30 are more flexible? Use \(\alpha\) = 0.05.
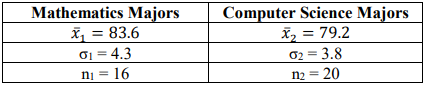
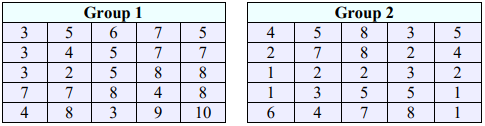
14. Two groups of students are given a problem-solving test, and the results are compared. Test the hypotheses that there is a difference in the test scores using the p-value method with \(\alpha\) = 0.05. Assume the populations are normally distributed.
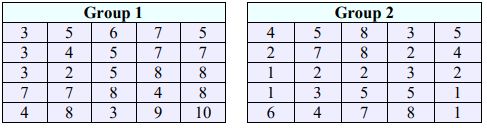
15. A survey found that the average daily cost to rent a car in Los Angeles is $103.24 and in Las Vegas is $97.24. The data were collected from two random samples of 40 in each of the two cities and the population standard deviations are $5.98 for Los Angeles and $4.21 for Las Vegas. At the 0.05 level of significance, construct a confidence interval for the difference in the means and then decide if there is a significant difference in the rates between the two cities using the confidence interval method.
For exercises 16-26, show all 5 steps for hypothesis testing:
a) State the hypotheses.
b) Compute the test statistic.
c) Compute the critical value or p-value.
d) State the decision.
e) Write a summary.
16. In a random sample of 50 Americans five years ago, the average credit card debt was $5,798 with a standard deviation of $1,154. In a random sample of 50 Americans in the present day, the average credit card debt is $6,511, with a standard deviation of $1,645. Using a 0.05 level of significance, test if there is a difference in credit card debt today versus five years ago. Assume the population variances are unequal.
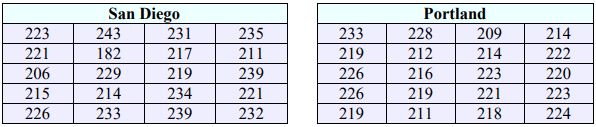
17. A movie theater company wants to see if there is a difference in the average movie ticket sales in San Diego and Portland per week. They sample 20 sales from San Diego and 20 sales from Portland over a week. Test the claim using a 5% level of significance. Assume the population variances are unequal, the samples are independent, and that movie sales are normally distributed.
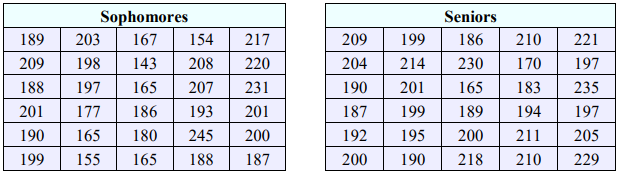
18. A researcher is curious what year in college students make use of the gym at a university. They take a random sample of 30 days and count the number of sophomores and seniors who use the gym each day. Is there evidence to suggest that a difference exists in gym usage based on year in college? Construct a confidence interval for the data below to decide. Use \(\alpha\) = 0.10. Assume the population variances are unequal.
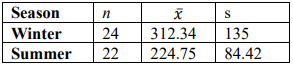
19. A national food product company believes that it sells more frozen pizza during the winter months than during the summer months. Weekly samples of sales found the following statistics in volume of sales (in hundreds of pounds). Use \(\alpha\) = 0.10. Use the p-value method to test the company’s claim. Assume the populations are approximately normally distributed with unequal variances.
20. You are testing the claim that the mean GPA of students who take evening classes is less than the mean GPA of students who only take day classes. You sample 20 students who take evening classes, and the sample mean GPA is 2.74 with a standard deviation of 0.86. You sample 25 students who only take day classes, and the sample mean GPA is 2.86 with a standard deviation of 0.54. Test the claim using a 10% level of significance. Assume the population standard deviations are unequal and that GPAs are normally distributed.
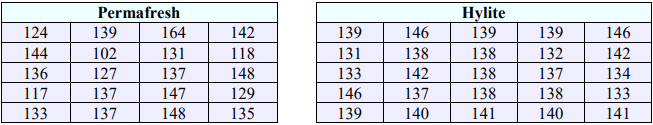
21. "Durable press" cotton fabrics are treated to improve their recovery from wrinkles after washing. "Wrinkle recovery angle" measures how well a fabric recovers from wrinkles. Higher scores are better. Here are data on the wrinkle recovery angle (in degrees) for a random sample of fabric specimens. Assume the populations are approximately normally distributed with unequal variances. A manufacturer believes that the mean wrinkle recovery angle for Hylite is better. A random sample of 20 Permafresh (group 1) and 25 Hylite (group 2) were measured. Test the claim using a 10% level of significance.
22. A large fitness center manager wants to test the claim that the mean delivery time for REI is faster than the delivery time for Champs Sports. The manager randomly samples 30 REI delivery times and finds a mean of 3.05 days with a standard deviation of 0.75 days. The manager randomly selects 30 Champs Sports delivery times and finds a mean delivery time of 3.262 days with a standard deviation of 0.27 days. Test the claim using a 5% level of significance. Assume the populations variances are unequal.
23. Two competing fast food restaurants advertise that they have the fastest wait time from when you order to when you receive your meal. A curious critic takes a random sample of 40 customers at each restaurant to test the claim. They find that Restaurant A has a sample mean wait time of 2.25 minutes with a standard deviation of 0.35 minutes and Restaurant B has a sample mean wait time of 2.15 minutes with a standard deviation of 0.57 minutes in wait time. Can they conclude that the mean wait time is significantly different for the two restaurants? Test at \(\alpha\) = 0.05. Assume the population variances are unequal.
24. The manager at a pizza place has been getting complaints that the auto-fill soda machine is either under filling or over filling their cups. The manager took a random sample of 20 fills from her machine, and a random sample of 20 fills from another branch of the restaurant that has not been having complaints. From her machine, she found a sample mean of 11.5 oz. with a standard deviation of 1.3 oz. and from the other restaurant’s machine she found a sample mean of 10.95 oz. with a standard deviation of 0.65 oz. At the 0.05 level of significance, does it seem her machine has a significantly different mean than the other machine? Use the confidence interval method. Assume the populations are normally distributed with unequal variances.
25. A new over-the-counter medicine to treat a sore throat is to be tested for effectiveness. The makers of the medicine take two random samples of 25 individuals showing symptoms of a sore throat. Group 1 receives the new medicine and Group 2 receives a placebo. After a few days on the medicine, each group is interviewed and asked how they would rate their comfort level 1-10 (1 being the most uncomfortable and 10 being no discomfort at all). The results are below. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude the mean scores from Group 1 is more than Group 2? Test at \(\alpha\) = 0.01. Assume the populations are normally distributed and have unequal variances.
26. In a random sample of 60 pregnant women with preeclampsia, their systolic blood pressure was taken right before beginning to push during labor. The mean systolic blood pressure was 174 with a standard deviation of 12. In another random sample of 80 pregnant women without preeclampsia, there was a mean systolic blood pressure of 133 and a standard deviation of 8 when the blood pressure was also taken right before beginning to push. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude that women with preeclampsia have a higher mean blood pressure in the late stages of labor? Test at the 0.01 level of significance. Assume the population variances are unequal.
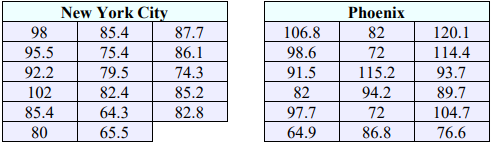
28. An employee at a large company is told that the mean starting salary at her company differs based on level of experience. The employee is skeptical and randomly samples 30 new employees with less than 5 years of experience and categorizes them as Group 1 and 30 new employees with 5 years of experience or more and categorizes them as Group 2. In Group 1, she finds the sample mean starting salary to be $50,352 with a standard deviation of $4,398.10. Group 2 has a sample mean starting salary of $52,391 with a standard deviation of $7,237.32. Test her claim at the 0.10 level of significance. Use the confidence interval method. Assume the populations are normally distributed with unequal variances.
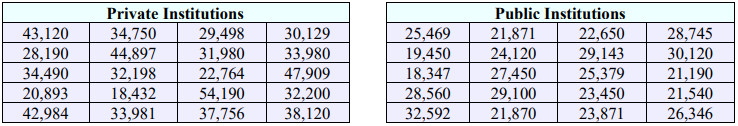
29. Two random samples are taken from private and public universities (out-of-state tuition) around the nation. The yearly tuition is recorded from each sample and the results can be found below. Find the 95% confidence interval for the mean difference between private and public institutions. Assume the populations are normally distributed and have unequal variances.
For exercises 30-33, show all 5 steps for hypothesis testing:
a) State the hypotheses.
b) Compute the test statistic.
c) Compute the critical value or p-value.
d) State the decision.
e) Write a summary.
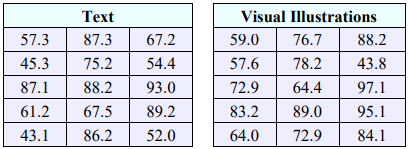
30. A professor wants to know if there is a difference in comprehension of a lab assignment among students depending if the instructions are given all in text, or if they are given primarily with visual illustrations. She randomly divides her class into two groups of 15, gives one group instructions in text and the second group instructions with visual illustrations. The following data summarizes the scores the students received on a test given after the lab. Assume the populations are normally distributed with equal variances. Is there evidence to suggest that a difference exists in the comprehension of the lab based on the test scores? Use \(\alpha\) = 0.10.
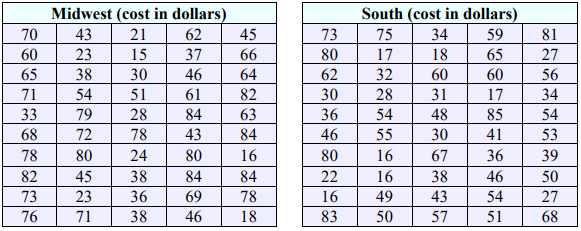
31. A large shoe company is interested in knowing if the amount of money a customer is willing to pay on a pair of shoes is different depending on location. They take a random sample of 50 single-pair purchases from Southern states and another random sample of 50 single-pair purchases from Midwestern states and record the cost for each. The results can be found below. At the 0.05 level of significance, is there evidence that the mean cost differs between the Midwest and the South? Assume the population variances are equal.
32. The manager at a local coffee shop is trying to decrease the time customers wait for their orders. He wants to find out if keeping multiple registers open will make a difference. He takes a random sample of 30 customers when only one register is open and finds that they wait an average of 6.4 minutes to reach the front with a standard deviation of 1.34 minutes. He takes another random sample of 35 customers when two registers are open and finds that they wait an average of 4.2 minutes to reach the front with a standard deviation of 1.21 minutes. He takes both his samples during peak hours to maintain consistency. Can it be concluded at the 0.05 level of significance that mean wait time is less with two registers open? Assume the population variances are equal.
33. The CEO of a large manufacturing company is curious if there is a difference in productivity level of her warehouse employees based on the region of the country the warehouse is located in. She randomly selects 35 employees who work in warehouses on the East Coast and 35 employees who work in warehouses in the Midwest and records the number of parts shipped out from each for a week. She finds that East Coast group ships an average of 1,287 parts and a standard deviation of 348. The Midwest group ships an average of 1,449 parts and a standard deviation of 298. Using a 0.01 level of significance, test if there is a difference in productivity level. Assume the population variances are equal.
34. In a random sample of 100 college students, 47 were sophomores and 53 were seniors. The sophomores reported spending an average of $37.03 per week going out for food and drinks with a standard deviation of $7.23, while the seniors reported spending an average of $52.94 per week going out for food and drinks with a standard deviation of $12.33. Find the 90% confidence interval for difference in the mean amount spent on food and drinks between sophomores and seniors? Assume the population variances are equal.
35. A pet store owner believes that dog owners, on average spend a different amount on their pets compared to cat owners. The owner randomly records the sales of 40 customers who said they only owned dogs and found the mean of the sales of $56.07 with a standard deviation of $24.50. The owner randomly records the sales of 40 customers who said they only owned cats and found a mean of the sales of $52.92 with a standard deviation of $23.53. Find the 95% confidence interval to test the pet store owner’s claim. Assume the population variances are equal.
For exercises 36-42, show all 5 steps for hypothesis testing:
a) State the hypotheses.
b) Compute the test statistic.
c) Compute the critical value or p-value.
d) State the decision.
e) Write a summary.
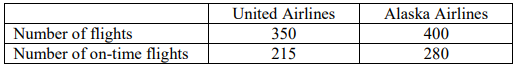
36. A researcher wants to see if there is a difference in the proportion of on-time flights for two airlines. Test the claim using \(\alpha\) = 0.10.
37. A random sample of 406 college freshmen found that 295 bought most of their textbooks from the college's bookstore. A random sample of 772 college seniors found that 537 bought their textbooks from the college's bookstore. You wish to test the claim that the proportion of all freshmen who purchase most of their textbooks from the college's bookstore is greater than the proportion of all seniors at a significance level of \(\alpha\) = 0.01.
38. To determine whether various antismoking campaigns have been successful, annual surveys are conducted. Randomly selected individuals are asked whether they smoke. The responses for this year had 163 out of 662 who smoked. Ten years ago, the survey found 187 out of 695 who smoked. Can we infer that the proportion of smokers has declined from 10 years ago? Use \(\alpha\) = 0.10.
39. TDaP is a booster shot that prevents Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis in adults and adolescents. The shot should be administered every 8 years in order for it to remain effective. A random sample of 500 people living in a town that experienced a pertussis outbreak this year were divided into two groups. Group 1 was made up of 132 individuals who had not had the TDaP booster in the past 8 years, and Group 2 consisted of 368 individuals who had. In Group 1, 15 individuals caught pertussis during the outbreak, and in Group 2, 11 individuals caught pertussis. Is there evidence to suggest that the proportion of individuals who caught pertussis and were not up to date on their booster shot is significantly higher than those that were? Test at the 0.05 level of significance.
40. The makers of a smartphone have received complaints that the facial recognition tool often does not work, or takes multiple attempts to finally unlock the phone. The company upgraded to a new version and are claiming the tool has improved. To test the claim, a critic takes a random sample of 75 users of the old version (Group 1) and 80 users of the new version (Group 2). They find that the facial recognition tool works on the first try 56% of the time in the old version and 70% of the time in the new version. Can it be concluded that the new version is performing better? Test at \(\alpha\) = 0.10.
41. In a sample of 80 faculty from Portland State University, it was found that 90% were union members, while in a sample of 96 faculty at University of Oregon, 75% were union members. Find the 95% confidence interval for the difference in the proportions of faculty that belong to the union for the two universities.
42. A random sample of 54 people who live in a city were selected and 16 identified as a "dog person." A random sample of 84 people who live in a rural area were selected and 34 identified as a "dog person." Test the claim that the proportion of people who live in a city and identify as a "dog person" is significantly different from the proportion of people who live in a rural area and identify as a "dog person" at the 10% significance level. Use the confidence interval method.
43. What is the critical value for a right-tailed F-test with a 5% level of significance with df1 = 4 and df2 = 33? Round answer to 4 decimal places.
44. What is the critical value for a right-tailed F-test with a 1% level of significance with df1 = 3 and df2 = 55? Round answer to 4 decimal places.
45. What is the critical value for a left-tailed F-test with a 10% level of significance with df1 = 29 and df2 = 20? Round answer to 4 decimal places.
46. What are the critical values for a two-tailed F-test with a 1% level of significance with df1 = 31 and df2 = 10? Round answer to 4 decimal places.
For exercises 47-61, show all 5 steps for hypothesis testing:
a) State the hypotheses.
b) Compute the test statistic.
c) Compute the critical value or p-value.
d) State the decision.
e) Write a summary.
47. A researcher wants to compare the variances of the heights (in inches) of four-year college basketball players with those of players in junior colleges. A sample of 30 players from each type of school is selected, and the variances of the heights for each type are 2.43 and 3.15 respectively. At \(\alpha\) = 0.10, test to see if there a significant difference between the variances of the heights in the two types of schools.
48. The marketing manager for a minor league baseball team suspects that there is a greater variance in game attendance during the spring months (April and May) than in the summer months (June, July, August). They take a random sample of 15 games in the spring and find that there is a mean attendance of 7,543 with a standard deviation of 87.4. In another random sample of 20 games in the summer, they find a mean attendance of 8,093 with a standard deviation of 56.2. Can the manager conclude that there is a greater variance in attendance in the spring? Test at \(\alpha\) = 0.05. Assume the populations are normally distributed.
49. A researcher takes sample temperatures in Fahrenheit of 17 days from New York City and 18 days from Phoenix. Test the claim that the standard deviation of temperatures in New York City is different from the standard deviation of temperatures in Phoenix. Use a significance level of \(\alpha\=0.05. Assume the populations are approximately normally distributed. You obtain the following two samples of data.
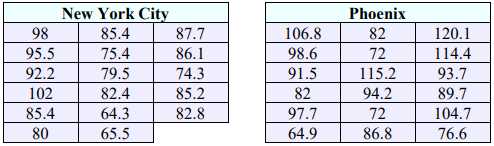
50. Two random samples are taken from private and public universities (out-of-state tuition) around the nation. The yearly tuition is recorded from each sample and the results can be found below. Private colleges are typically more expensive than public schools, however, a student is curious if the variance is different between the two. Can it be concluded that the variances of private and public tuition differ at the 0.05 level of significance? Assume the populations are normally distributed.
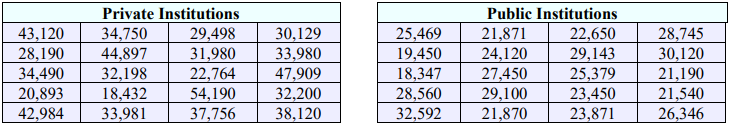
51. Two competing fast food restaurants advertise that they have the fastest wait time from when you order to when you receive your meal. A curious critic takes a random sample of 40 customers at each restaurant and finds that there is no statistically significant difference in the average wait time between the two restaurants. Both restaurants are in fact advertising truthfully then. However, as a skeptical statistician, this critic knows that a high standard deviation may also keep a customer waiting for a long time on any given trip to the restaurant, so they test for the difference in standard deviation of wait time from this same sample. They find that Restaurant A has a sample standard deviation of 0.35 minutes and Restaurant B has a sample standard deviation of 0.57 minutes in wait time. Can they conclude that the standard deviation in wait time is significantly longer for Restaurant B? Test at \(\alpha\) = 0.05.
52. A new over-the-counter medicine to treat a sore throat is to be tested for effectiveness. The makers of the medicine take two random samples of 25 individuals showing symptoms of a sore throat. Group 1 receives the new medicine and Group 2 receives a placebo. After a few days on the medicine, each group is interviewed and asked how they would rate their comfort level 1-10 (1 being the most uncomfortable and 10 being no discomfort at all). The results are below. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude the variance in scores from Group 1 is less than the variance in scores from Group 2? Test at \(\alpha\) = 0.01. Assume the populations are normally distributed.
53. The manager at a pizza place has been getting complaints that the auto-fill soda machine is either under filling or over filling their cups. The manager ran several tests on the machine before using it and knows that the average fill quantity is 12 oz. – exactly as she was hoping. However, she did not test the variance. She took a random sample of 20 fills from her machine, and a random sample of 20 fills from another branch of the restaurant that has not been having complaints. From her machine, she found a sample standard deviation of 1.3 oz. and from the other restaurant’s machine she found a sample standard deviation of 0.65 oz. At the 0.05 level of significance, does it seem her machine has a higher variance than the other machine? Assume the populations are normally distributed.
54. An employee at a large company believes that the variation in starting salary at her company differs based on level of experience. She randomly samples 30 new employees with less than 5 years of experience and categorizes them as Group 1 and 30 new employees with 5 years of experience or more and categorizes them as Group 2. In Group 1, she finds the sample standard deviation in starting salary to be $4,398.10 and in Group 2 she finds the sample standard deviation in starting salary to be $7,237.32. Test her claim at the 0.10 level of significance. Assume the populations are normally distributed.
55. In a random sample of 100 college students, 47 were sophomores and 53 were seniors. The sophomores reported spending an average of $37.03 per week going out for food and drinks with a standard deviation of $7.23, while the seniors reported spending an average of $52.94 per week going out for food and drinks with a standard deviation of $12.33. Can it be concluded that there is a difference in the standard deviation spent on food and drinks between sophomores and seniors? Test at \(\alpha\) = 0.10.
56. A large shoe company is interested in knowing if the amount of money a customer is willing to pay on a pair of shoes varies differently depending on location. They take a random sample of 50 single-pair purchases from Southern states and another random sample of 50 single-pair purchases from Midwestern states and record the cost for each. The results can be found below. At the 0.05 level of significance, is there evidence that the variance in cost differs between the Midwest and the South?
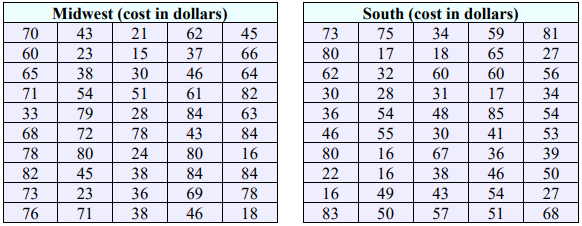
57. The math department chair at a university is proud to boast an average satisfaction score of 8.4 out of 10 for her department’s courses. This year, the English department advertised an average of 8.5 out of 10. Not to be outdone, the math department chair decides to check if there is a difference in how the scores vary between the departments. She takes a random sample of 65 math department evaluations and finds a sample standard deviation of 0.75 and a random sample of 65 English department evaluations and finds a sample standard deviation of 1.04. Does she have sufficient evidence to claim that the English department may have a higher average, but also has a higher standard deviation – meaning that their scores are not as consistent as the math department’s? Test at \(\alpha\) = 0.05.
58. An investor believes that investing in international stock is riskier because the variation in the rate of return is greater. She takes two random samples of 15 months over the past 30 years and finds the following rates of return from a selection of her own domestic and international investments. Can she conclude that the standard deviation in International Rate of Return is higher at the 0.10 level of significance? Assume the populations are normally distributed.
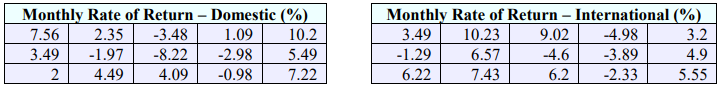
59. The manager at a local coffee shop is trying to decrease the time customers wait for their orders. He wants to find out if keeping multiple registers open will make a difference. He takes a random sample of 30 customers when only one register is open and finds that they wait an average of 6.4 minutes to reach the front with a standard deviation of 1.34 minutes. He takes another random sample of 35 customers when two registers are open and finds that they wait an average of 4.2 minutes to reach the front with a standard deviation of 1.21 minutes. He takes both his samples during peak hours to maintain consistency. Can it be concluded at the 0.05 level of significance that there is a smaller standard deviation in wait time with two registers open?
60. A movie theater company wants to see if there is a difference in the variance of movie ticket sales in San Diego and Portland per week. They sample 20 sales from San Diego and 20 sales from Portland and count the number of tickets sold over a week. Test the claim using a 5% level of significance. Assume that movie sales are normally distributed.
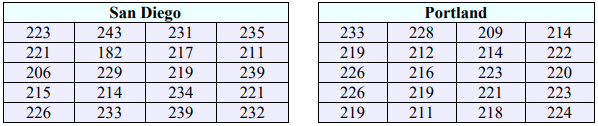
61. In a random sample of 60 pregnant women with preeclampsia, their systolic blood pressure was taken right before beginning to push during labor. The mean systolic blood pressure was 174 with a standard deviation of 12. In another random sample of 80 pregnant women without preeclampsia, there was a mean systolic blood pressure of 133 and a standard deviation of 8 when the blood pressure was also taken right before beginning to push. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude that women with preeclampsia have a larger variation in blood pressure in the late stages of labor? Test at the 0.01 level of significance.
Trillian punched up the figures. They showed two‐to‐the power‐of-Infinity-minus‐one (an irrational number that only has a conventional meaning in Improbability physics).
"... it's pretty low," continued Zaphod with a slight whistle.
"Yes," agreed Trillian, and looked at him quizzically.
"That's one big whack of Improbability to be accounted for. Something pretty improbable has got to show up on the balance sheet if it's all going to add up into a pretty sum."
Zaphod scribbled a few sums, crossed them out and threw the pencil away.
"Bat's dots, I can't work it out."
"Well?"
Zaphod knocked his two heads together in irritation and gritted his teeth.
"OK," he said. "Computer!"
(Adams, 2002)
- Answers to Odd Numbered Exercises
-
1) H0: µD = 0; H1: µD < 0; t = -0.7514; p-value = 0.2311; Do not reject H0. There is not enough evidence to support the claim on average the new online learning module increased placement scores.
3) H0: µD = 0; H1: µD > 0; t = 3.5598; p-value = 0.001; Reject H0. There is enough evidence to support the claim that the mean time to complete a task decreases when workers are allowed to wear their ear buds.
5) H0: µD = 0; H1: µD > 0; t = 4.7951; p-value = 0.0001; Reject H0. There is enough evidence to support the claim that the mean reaction time is significantly faster for a person’s dominant hand.
7) a) -11.9129 < µD < -8.4871 b) Yes, since µD = 0 is not captured in the interval (-11.9129, -8.4871).
9) H0: µ1 = µ2; H1: µ1 < µ2; z = -3.0908; pvalue = 0.001; Reject H0. There is enough evidence to support the claim that the online homework system for introductory math courses improved student’s average test scores.
11) H0: µ1 = µ2; H1: µ1 > µ2; z = 0.5602; p-value = 0.2877; Do not reject H0. There is not enough evidence to support the claim that the American League team would score on average more runs for games in which the designated hitter was used.
13) H0: µ1 = µ2; H1: µ1 > µ2; z = 3.0444; p-value = 0.0012; Reject H0. There is enough evidence to support the claim that adults under the age of 30 are more flexible.
15) H0: µ1 = µ2; H1: µ1 ≠ µ2; 3.7336 < µ1 - µ2 < 8.2664; Reject H0. There is a statistically significant difference in the mean daily car rental cost between Las Angeles and Las Vegas at the 5% level of significance.
17) H0: µ1 = µ2; H1: µ1 ≠ µ2; t = 1.0624; p-value = 0.2978; fail to reject H0. There is not enough evidence to support the claim that there is a difference in the average movie ticket sales in San Diego and Portland per week.
19) H0: µ1 = µ2; H1: µ1 > µ2; t = 2.6612; p-value = 0.0056; Reject H0. There is enough evidence to support the claim that the mean number of frozen pizzas sold during the winter months is more than during the summer months.
21) H0: µ1 = µ2; H1: µ1 < µ2; t = -1.2639; p-value = 0.1098; Do not reject H0. There is not enough evidence to support the claim that the mean wrinkle recovery angle for Hylite is better than Permafresh.
23) H0: µ1 = µ2; H1: µ1 ≠ µ2; t = 0.9455; p-value = 0.3479; Do not reject H0. There is not enough evidence to support the claim that the mean wait time for the two restaurants is different.
25) H0: µ1 = µ2; H1: µ1 ≠ µ2; t = 22.9197; Reject H0. There is enough evidence to support the claim that the soda machine is different from the other restaurants.
27) H0: µ1 = µ2; H1: µ1 ≠ µ2; -16.3925 < µ1 - µ2 < -1.1153; Reject H0. There is enough evidence to support the claim that women with preeclampsia have a higher mean blood pressure in the late stages of labor.
29) $5,070.33 < µ1 - µ2 < $14,049.47
31) H0: µ1 = µ2; H1: µ1 ≠ µ2; t = 2.0435; p-value = 0.0437; Reject H0. There is enough evidence to support the claim that the mean cost for a pair of shoes in the Midwest and the South are different.
33) H0: µ1 = µ2; H1: µ1 ≠ µ2; t = -2.0919; p-value = 0.0402; Do not reject H0. There is not enough evidence to support the claim that there is a statistically significant difference in the mean productivity level between the two locations.
35) H0: µ1 = µ2; H1: µ1 ≠ µ2; -7.5429 < µ1 - µ2 < 13.8429; Do not reject H0. There is not enough evidence to support the claim that dog owners spend more on average than cat owners on their pets.
37) H0: µ1 = µ2; H1: p1 > p2; z = 1.1104; p-value = 0.1334; Do not reject H0. There is not enough evidence to support the claim that the proportion of all freshman that purchase most of their textbooks from the college's bookstore is greater than the proportion of all seniors.
39) H0: µ1 = µ2; H1: p1 > p2; z = 3.7177; p-value = 0.0001; Reject H0. Yes, there is evidence that the proportion of those who caught pertussis is higher for those who were not up to date on their booster.
41) 0.04126 < p1 – p2 < 0.25874
43) 2.6589
45) 0.5967
47) H0: \(\sigma_{1}^{2}=\sigma_{2}^{2}\) ; H1: \(\sigma_{1}^{2} \neq \sigma_{2}^{2}\) ; F = 0.7714; pvalue = 0.4891; Do not reject H0. There is not enough evidence to support the claim that there a significant difference between the variances of the heights of four-year college basketball players with those of players in junior colleges.
49) H0: σ1 = σ2; H1: σ1 ≠ σ2; F = 0.4154; CV = 0.3652 & 2.6968; Do not reject H0. There is not enough evidence to support the claim that there a significant difference between the standard deviation of temperatures in New York City compared to Phoenix.
51) H0: σ1 = σ2; H1: σ1 < σ2; F = 0.377; p-value = 0.0015; Reject H0. There is enough evidence to support the claim that the standard deviation of wait times for Restaurant B is significantly longer than Restaurant A.
53) H0: \(\sigma_{1}^{2}=\sigma_{2}^{2}\) ; H1: \(\sigma_{1}^{2}=\sigma_{2}^{2}\) ; F = 4; p-value = 0.002; Reject H0. There is enough evidence to support the claim that the soda machine has a higher variance compared to the other restaurant.
55) H0: σ1 = σ2; H1: σ1 ≠ σ2; F = 0.3438; p-value = 0.0003; Reject H0. There is enough evidence to claim that the standard deviation in money spent on food and drinks differs between sophomores and seniors.
57) H0: σ1 = σ2; H1: σ1 < σ2; F = 0.5201; p-value = 0.0049; Reject H0. There is enough evidence to claim that the standard deviation in satisfaction scores is higher for the English department compared to the Math department.
59) H0: σ1 = σ2; H1: σ1 > σ2; F = 1.2264; p-value = 0.282; Do not reject H0. There is not enough evidence to claim that the standard deviation in wait time with two registers open is smaller.
61) H0: σ1 = σ2; H1: σ1 > σ2; F = 2.25; p-value = 0.0004; Reject H0. There is evidence to claim that the standard deviation in blood pressure for women with preeclampsia has a larger variation in the late stages of labor.


