6.7: Chapter 6 Formulas
- Page ID
- 26657
|
Uniform Distribution \(f(x)=\frac{1}{b-a}, \text { for } a \leq x \leq b\)
|
Exponential Distribution \(f(x)=\frac{1}{\mu} e^{\left(-\frac{x}{\mu}\right)}, \text { for } x \geq 0\)
|
|
Standard Normal Distribution \(\mu=0, \sigma=1\) |
Central Limit Theorem \(Z \text {-score: } z=\frac{\bar{x}-\mu}{\left(\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}\right)}\) |
| Normal Distribution Probabilities: |
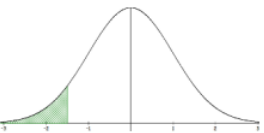
P(X ≤ x) = P(X < x)
Excel: =NORM.DIST(x,µ,σ,true) TI-84: normalcdf(-1E99,x,µ,σ) |
|
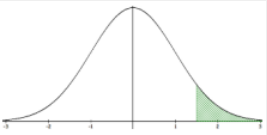
P(X ≥ x) = P(X > x)
Excel: = 1–NORM.DIST(x,µ,σ,true) TI-84: normalcdf(x,1E99,µ,σ) |
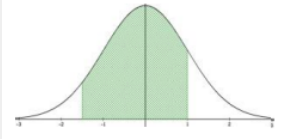
P(x1 ≤ X ≤ x2) = P(x1 < X < x2) =
Excel: =NORM.DIST(x2,µ,σ,true)- NORM.DIST(x1,µ,σ,true) TI-84: normalcdf(x1,x2,µ,σ) |
| Percentiles for Normal Distribution: |
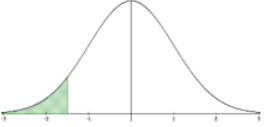
P(X ≤ x) = P(X < x)
Excel: =NORM.INV(area,µ,σ) TI-84: invNorm(area,µ,σ) |
|
P(X ≥ x) = P(X > x)
Excel: =NORM.INV(1–area,µ,σ) TI-84: invNorm(1–area,µ,σ) |
P(x1 ≤ X ≤ x2) = P(x1 < X < x2) =
Excel: x1 =NORM.INV((1–area)/2,µ,σ) x2 =NORM.INV(1–((1–area)/2),µ,σ) TI-84: x1 = invNorm((1–area)/2,µ,σ) x2 =invNorm(1–((1–area)/2),µ,σ) |