2.6: The Precise Definition of a Limit
- Page ID
- 25930
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Learning Objectives
- Describe the epsilon-delta definition of a limit.
- Apply the epsilon-delta definition to find the limit of a function.
- Describe the epsilon-delta definitions of one-sided limits and infinite limits.
- Use the epsilon-delta definition to prove the limit laws.
By now you have progressed from the very informal definition of a limit in the introduction of this chapter to the intuitive understanding of a limit. At this point, you should have a very strong intuitive sense of what the limit of a function means and how you can find it. In this section, we convert this intuitive idea of a limit into a formal definition using precise mathematical language. The formal definition of a limit is quite possibly one of the most challenging definitions you will encounter early in your study of calculus; however, it is well worth any effort you make to reconcile it with your intuitive notion of a limit. Understanding this definition is the key that opens the door to a better understanding of calculus.
Quantifying Closeness
Before stating the formal definition of a limit, we must introduce a few preliminary ideas. Recall that the distance between two points \(a\) and \(b\) on a number line is given by |\(a−b\)|.
- The statement |\(f(x)−L\)|<ε may be interpreted as: The distance between \(f(x)\) and \(L\) is less than \(ε\).
- The statement \(0<|x−a|<δ\) may be interpreted as: \(x≠a\) and the distance between \(x\) and \(a\) is less than \(δ\).
It is also important to look at the following equivalences for absolute value:
- The statement |\(f(x)−L|<ε\) is equivalent to the statement \(L−ε<f(x)<L+ε\).
- The statement \(0<|x−a|<δ\) is equivalent to the statement \(a−δ<x<a+δ\) and \(x≠a\).
With these clarifications, we can state the formal epsilon-delta definition of the limit.
Definition: Finite Limits (Formal)
Let \(f(x)\) be defined for all \(x≠a\) over an open interval containing \(a\). Let \(L\) be a real number. Then
\[\lim_{x→a}f(x)=L\]
if, for every \(ε>0\), there exists a \(δ>0\), such that if \(0<|x−a|<δ\), then \(|f(x)−L|<ε\).
This definition may seem rather complex from a mathematical point of view, but it becomes easier to understand if we break it down phrase by phrase. The statement itself involves something called a universal quantifier (for every \(ε>0\)), an existential quantifier (there exists a \(δ>0\)), and, last, a conditional statement (if \(0<|x−a|<δ\), then \(|f(x)−L|<ε)\). Let’s take a look at Table \(\PageIndex{1}\), which breaks down the definition and translates each part.
| Definition | Translation |
|---|---|
| 1. For every \(ε>0\), | 1. For every positive distance \(ε\) from L, |
| 2. there exists a \(δ>0\), | 2. There is a positive distance \(δ\) from a, |
| 3. such that | 3. such that |
| 4. if \(0<|x−a|<δ\), then \(|f(x)−L|<ε\). | 4. if \(x\) is closer than \(δ\) to a and \(x≠a\), then \(f(x)\) is closer than ε to L. |
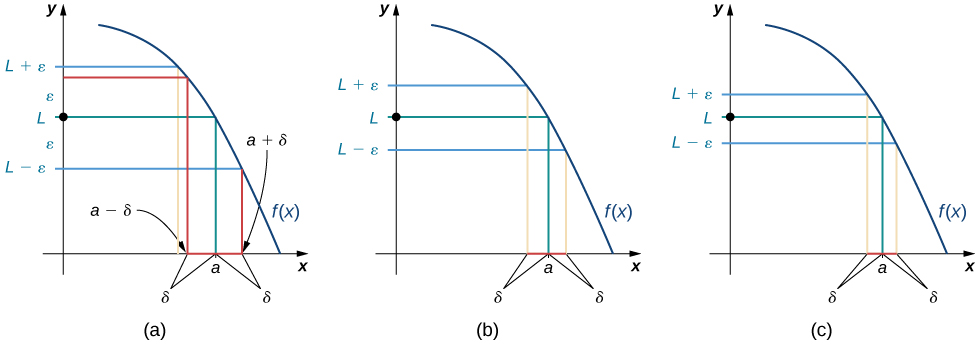
We can get a better handle on this definition by looking at the definition geometrically. Figure shows possible values of \(δ\) for various choices of \(ε>0\) for a given function \(f(x)\), a number a, and a limit L at a. Notice that as we choose smaller values of ε (the distance between the function and the limit), we can always find a \(δ\) small enough so that if we have chosen an x value within \(δ\) of a, then the value of \(f(x)\) is within \(ε\) of the limit L.
Note
Visit the following applet to experiment with finding values of \(δ\) for selected values of \(ε\):
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\) shows how you can use this definition to prove a statement about the limit of a specific function at a specified value.
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\): Proving a Statement about the Limit of a Specific Function
Prove that \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→1} \;(2x+1)=3\).
Solution
Let \(ε>0\).
The first part of the definition begins “For every \(ε>0\).”This means we must prove that whatever follows is true no matter what positive value of ε is chosen. By stating “Let
\(ε>0\),” we signal our intent to do so.
Choose \(δ=\frac{ε}{2}\).
The definition continues with “there exists a \(δ>0\). ” The phrase “there exists” in a mathematical statement is always a signal for a scavenger hunt. In other words, we must go and find \(δ\). So, where exactly did \(δ=ε/2\) come from? There are two basic approaches to tracking down \(δ\). One method is purely algebraic and the other is geometric.
We begin by tackling the problem from an algebraic point of view. Since ultimately we want \(|(2x+1)−3|<ε\), we begin by manipulating this expression: \(|(2x+1)−3|<ε\) is equivalent to \(|2x−2|<ε\), which in turn is equivalent to \(|2||x−1|<ε\). Last, this is equivalent to \(|x−1|<ε/2\). Thus, it would seem that \(δ=ε/2\) is appropriate.
We may also find \(δ\) through geometric methods. Figure demonstrates how this is done.

Assume \(0<|x−1|<δ\). When \(δ\) has been chosen, our goal is to show that if \(0<|x−1|<δ\), then \(|(2x+1)−3|<ε\). To prove any statement of the form “If this, then that,” we begin by assuming “this” and trying to get “that.”
Thus,
\(|(2x+1)−3|=|2x−2|\) property of absolute value
\(=|2(x−1)|\)
\(=|2||x−1|\) \(|2|=2\)
\(=2|x−1|\)
\(<2⋅δ \) here’s where we use the assumption that \(0<|x−1|<δ\)
\(=2⋅\frac{ε}{2}=ε\) here’s where we use our choice of \(δ=ε/2\)
Analysis
In this part of the proof, we started with \(|(2x+1)−3|\) and used our assumption \(0<|x−1|<δ\) in a key part of the chain of inequalities to get \(|(2x+1)−3|\) to be less than ε. We could just as easily have manipulated the assumed inequality \(0<|x−1|<δ\) to arrive at \(|(2x+1)−3|<ε\) as follows:
\(0<|x−1|<δ⇒|x−1|<δ\)
\(⇒−δ<x−1<δ\)
\(⇒−\frac{ε}{2}<x−1<\frac{ε}{2}\)
\(⇒−ε<2x−2<ε\)
\(⇒−ε<2x−2<ε\)
\(⇒|2x−2|<ε\)
\(⇒|(2x+1)−3|<ε.\)
Therefore, \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→1} \;(2x+1)=3.\) (Having completed the proof, we state what we have accomplished.)
After removing all the remarks, here is a final version of the proof:
Let \(ε>0\).
Choose \(δ=ε/2\).
Assume \(0<|x−1|<δ\).
Thus,
\(\begin{align*} |(2x+1)−3| &= |2x−2|\\[4pt]
&=|2(x−1)|\\[4pt]
&=|2||x−1|\\[4pt]
&=2|x−1|\\[4pt]
&<2⋅δ\\[4pt]
&=2⋅\frac{ε}{2}\\[4pt]
&=ε. \end{align*}\)
Therefore, \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→1} \;(2x+1)=3\).
The following Problem-Solving Strategy summarizes the type of proof we worked out in Example \(\PageIndex{2}\).
The following Problem-Solving Strategy summarizes the type of proof we worked out in Example.
Problem-Solving Strategy: Proving That \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→a}f(x)=L\) for a Specific Function \(f(x)\)
- Let’s begin the proof with the following statement: Let \(ε>0\).
- Next, we need to obtain a value for \(δ\). After we have obtained this value, we make the following statement, filling in the blank with our choice of \(δ\): Choose \(δ=\)_______.
- The next statement in the proof should be (at this point, we fill in our given value for \(a\)): Assume \(0<|x−a|<δ\).
- Next, based on this assumption, we need to show that \(|f(x)−L|<ε\), where \(f(x)\) and \(L\) are our function \(f(x)\) and our limit \(L\). At some point, we need to use \(0<|x−a|<δ\).
- We conclude our proof with the statement: Therefore, \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→a}f(x)=L\).
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\): Proving a Statement about a Limit
Complete the proof that \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→−1}\;(4x+1)=−3\) by filling in the blanks.
Let _____.
Choose \(δ=\)_______.
Assume \(0<|x\)−_______|\(<δ\).
Thus, |________−________|=_____________________________________\(ε\).
Solution
We begin by filling in the blanks where the choices are specified by the definition. Thus, we have
Let \(ε>0\).
Choose \(δ\)=_______.
Assume \(0<|x−(−1)|<δ\). (or equivalently, \(0<|x+1|<δ\).)
Thus, \(|(4x+1)−(−3)|=|4x+4|=|4||x+1|<4δ\)_______\(ε\).
Focusing on the final line of the proof, we see that we should choose \(δ=\frac{ε}{4}\).
We now complete the final write-up of the proof:
Let \(ε>0\).
Choose \(δ=\frac{ε}{4}\).
Assume \(0<|x−(−1)|<δ\) (or equivalently, \(0<|x+1|<δ\).)
Thus, \(|(4x+1)−(−3)|=|4x+4]|=|4||x+1|<4δ=4(ε/4)=ε\).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Complete the proof that \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→2}\;(3x−2)=4\) by filling in the blanks.
Let _______.
Choose \(δ\) =_______.
Assume \(0<|x−\)____\(|<\)____.
Thus,
|_______−____|\(=\)______________________________\(ε\).
Therefore, \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→2}\;(3x−2)=4\).
- Hint
-
Follow the outline in the Problem-Solving Strategy that we worked out in full in Example \(\PageIndex{3}\).
- Answer
-
Let \(ε>0\); choose \(δ=\frac{ε}{3}\); assume \(0<|x−2|<δ\).
Thus, \(|(3x−2)−4|=|3x−6|=|3|⋅|x−2|<3⋅δ=3⋅(ε/3)=ε\).
Therefore, \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→2}(3x−2)=4\).
In Examples \(\PageIndex{1}\) and \(\PageIndex{2}\), the proofs were fairly straightforward, since the functions with which we were working were linear. In Example \(\PageIndex{4}\), we see how to modify the proof to accommodate a nonlinear function.
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\): Proving a Statement about the Limit of a Specific Function (Geometric Approach)
Prove that \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→2}x^2=4\).
Solution
1. Let \(ε>0\). The first part of the definition begins “For every \(ε>0\),” so we must prove that whatever follows is true no matter what positive value of \(ε\) is chosen. By stating “Let \(ε>0\),” we signal our intent to do so.
2. Without loss of generality, assume \(ε≤4\). Two questions present themselves: Why do we want \(ε≤4\) and why is it okay to make this assumption? In answer to the first question: Later on, in the process of solving for \(δ\), we will discover that \(δ\) involves the quantity \(\sqrt{4−ε}\). Consequently, we need \(ε≤4\). In answer to the second question: If we can find \(δ>0\) that “works” for \(ε≤4\), then it will “work” for any \(ε>4\) as well. Keep in mind that, although it is always okay to put an upper bound on ε, it is never okay to put a lower bound (other than zero) on \(ε\).
3. Choose \(δ=min {2−\sqrt{4−ε},\sqrt{4+ε}−2}\). Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\) shows how we made this choice of \(δ\).
![This graph shows how to find delta geometrically for a given epsilon for the above proof. First, the function f(x) = x^2 is drawn from [-1, 3]. On the y axis, the proposed limit 4 is marked, and the line y=4 is drawn to intersect with the function at (2,4). For a given epsilon, point 4 + epsilon and 4 – epsilon are marked on the y axis above and below 4. Blue lines are drawn from these points to intersect with the function, where pink lines are drawn from the point of intersection to the x axis. These lines land on either side of x=2. Next, we solve for these x values, which have to be positive here. The first is x^2 = 4 – epsilon, which simplifies to x = sqrt(4-epsilon). The next is x^2 = 4 + epsilon, which simplifies to x = sqrt(4 + epsilon). Delta is the smaller of the two distances, so it is the min of (2 – sqrt(4 – epsilon) and sqrt(4 + epsilon) – 2).](https://stats.libretexts.org/@api/deki/files/14910/2.5.2.png?revision=1)
4. We must show: If \(0<|x−2|<δ\), then \(|x^2−4|<ε\), so we must begin by assuming
\(0<|x−2|<δ.\)
We don’t really need \(0<|x−2|\) (in other words, \(x≠2\)) for this proof. Since \(0<|x−2|<δ⇒|x−2|<δ\), it is okay to drop \(0<|x−2|\).
\(|x−2|<δ.\)
Hence,
\(−δ<x−2<δ.\)
Recall that \(δ=min\){\(2−\sqrt{4−ε},\sqrt{4+ε}−2\)}. Thus, \(δ≥2−\sqrt{4−ε}\) and consequently \(−(2−\sqrt{4−ε})≤−δ\). We also use \(δ≤\sqrt{4+ε}−2\) here. We might ask at this point: Why did we substitute \(2−\sqrt{4−ε}\) for \(δ\) on the left-hand side of the inequality and \(\sqrt{4+ε}−2\) on the right-hand side of the inequality? If we look at Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\), we see that \(2−\sqrt{4−ε}\) corresponds to the distance on the left of \(2\) on the \(x\)-axis and \(\sqrt{4+ε}−2\) corresponds to the distance on the right. Thus,
\(−(2−\sqrt{4−ε})≤−δ<x−2<δ≤\sqrt{4+ε}−2.\)
We simplify the expression on the left:
\(−2+\sqrt{4−ε}<x−2<\sqrt{4+ε}−2\).
Then, we add 2 to all parts of the inequality:
\(\sqrt{4−ε}<x<\sqrt{4+ε}.\)
We square all parts of the inequality. It is okay to do so, since all parts of the inequality are positive:
\(4−ε<x^2<4+ε.\)
We subtract \(4\) from all parts of the inequality:
\(−ε<x^2−4<ε.\)
Last,
\(|x^2−4|<ε.\)
5. Therefore,
\(\displaystyle \lim_{x→2}x^2=4.\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Find δ corresponding to \(ε>0\) for a proof that \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→9}\sqrt{x}=3\).
- Hint
-
Draw a graph similar to the one in Example \(\PageIndex{4}\).
- Answer
-
Choose \(δ=\text{min}\{9−(3−ε)^2,\;(3+ε)^2−9\}\).
The geometric approach to proving that the limit of a function takes on a specific value works quite well for some functions. Also, the insight into the formal definition of the limit that this method provides is invaluable. However, we may also approach limit proofs from a purely algebraic point of view. In many cases, an algebraic approach may not only provide us with additional insight into the definition, it may prove to be simpler as well. Furthermore, an algebraic approach is the primary tool used in proofs of statements about limits. For Example \(\PageIndex{5}\), we take on a purely algebraic approach.
Example \(\PageIndex{5}\):Proving a Statement about the Limit of a Specific Function (Algebraic Approach)
Prove that \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→−1}\;(x^2−2x+3)=6.\)
Solution
Let’s use our outline from the Problem-Solving Strategy:
1. Let \(ε>0\).
2. Choose \(δ=\text{min}\{1,ε/5\}\). This choice of \(δ\) may appear odd at first glance, but it was obtained by taking a look at our ultimate desired inequality: \(∣(x^2−2x+3)−6∣<ε\). This inequality is equivalent to \(|x+1|⋅|x−3|<ε\). At this point, the temptation simply to choose \(δ=\frac{ε}{x−3}\) is very strong. Unfortunately, our choice of \(δ\) must depend on ε only and no other variable. If we can replace \(|x−3|\) by a numerical value, our problem can be resolved. This is the place where assuming \(δ≤1\) comes into play. The choice of \(δ≤1\) here is arbitrary. We could have just as easily used any other positive number. In some proofs, greater care in this choice may be necessary. Now, since \(δ≤1\) and \(|x+1|<δ≤1\), we are able to show that \(|x−3|<5\). Consequently, \(|x+1|⋅|x−3|<|x+1|⋅5\). At this point we realize that we also need \(δ≤ε/5\). Thus, we choose \(δ=\text{min}\{1,ε/5\}\).
3. Assume \(0<|x+1|<δ\). Thus,
\[|x+1|<1\text{ and }|x+1|<\frac{ε}{5}. \nonumber\]
Since \(|x+1|<1\), we may conclude that \(−1<x+1<1\). Thus, by subtracting \(4\) from all parts of the inequality, we obtain \(−5<x−3<−1\). Consequently, \(|x−3|<5\). This gives us
\[\left|(x^2−2x+3)−6\right|=|x+1|⋅|x−3|<\frac{ε}{5}⋅5=ε.\nonumber\]
Therefore,
\[\lim_{x→−1}\;(x^2−2x+3)=6.\nonumber\]
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Complete the proof that \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→1}x^2=1\).
Let \(ε>0\); choose \(δ=\text{min}\{1,ε/3\}\); assume \(0<|x−1|<δ\).
Since \(|x−1|<1\), we may conclude that \(−1<x−1<1\). Thus, \(1<x+1<3\). Hence, \(|x+1|<3\).
- Hint
-
Use Example \(\PageIndex{5}\) as a guide.
- Answer
-
\(∣x^2−1∣=|x−1|⋅|x+1|<ε/3⋅3=ε\)
You will find that, in general, the more complex a function, the more likely it is that the algebraic approach is the easiest to apply. The algebraic approach is also more useful in proving statements about limits.
Proving Limit Laws
We now demonstrate how to use the epsilon-delta definition of a limit to construct a rigorous proof of one of the limit laws. The triangle inequality is used at a key point of the proof, so we first review this key property of absolute value.
Definition: The Triangle Inequality
The triangle inequality states that if a and b are any real numbers, then \(|a+b|≤|a|+|b|\).
Proof
We prove the following limit law: If \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→a}f(x)=L\) and \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→a}g(x)=M\), then \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→a}\;(f(x)+g(x))=L+M\).
Let \(ε>0\).
Choose \(δ_1>0\) so that if \(0<|x−a|<δ_1\), then \(|f(x)−L|<ε/2\).
Choose \(δ_2>0\) so that if \(0<|x−a|<δ_2\), then \(|g(x)−M|<ε/2\).
Choose \(δ=\text{min}\{δ_1,δ_2\}\).
Assume \(0<|x−a|<δ\).
Thus,
\(0<|x−a|<δ_1\) and \(0<|x−a|<δ_2\).
Hence,
\[\begin{align*} |(f(x)+g(x))−(L+M)|&=|(f(x)−L)+(g(x)−M)|\\[4pt]
&≤|f(x)−L|+|g(x)−M|\\[4pt]
&<\frac{ε}{2}+\frac{ε}{2}=ε \end{align*}.\]
□
We now explore what it means for a limit not to exist. The limit \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→a}f(x)\) does not exist if there is no real number \(L\) for which \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→a}f(x)=L\). Thus, for all real numbers \(L\), \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→a}f(x)≠L\). To understand what this means, we look at each part of the definition of \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→a}f(x)=L\) together with its opposite. A translation of the definition is given in Table \(\PageIndex{2}\).
| Definition | Opposite |
|---|---|
| 1. For every \(ε>0\), | 1. There exists \(ε>0\) so that |
| 2. there exists a \(δ>0\), so that | 2. for every \(δ>0\), |
| 3. if \(0<|x−a|<δ\), then \(|f(x)−L|<ε\). | 3. There is an x satisfying \(0<|x−a|<δ\) so that \(|f(x)−L|≥ε\). |
Translation of the Definition of \(\lim_{x→a}f(x)=L\) and its Opposite
Finally, we may state what it means for a limit not to exist. The limit \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→a}f(x)\) does not exist if for every real number \(L\), there exists a real number \(ε>0\) so that for all \(δ>0\), there is an \(x\) satisfying \(0<|x−a|<δ\), so that \(|f(x)−L|≥ε\). Let’s apply this in Example \(\PageIndex{6}\) to show that a limit does not exist.
Example \(\PageIndex{6}\): Showing That a Limit Does Not Exist
Show that \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→0}\frac{|x|}{x}\) does not exist. The graph of \(f(x)=|x|/x\) is shown here:
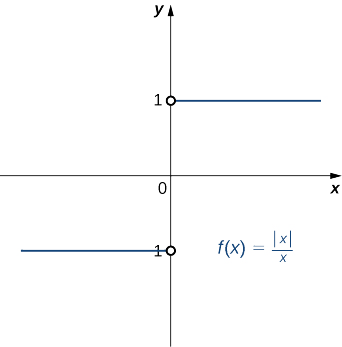
Solution
Suppose that \(L\) is a candidate for a limit. Choose \(ε=1/2\).
Let \(δ>0\). Either \(L≥0\) or \(L<0\). If \(L≥0\), then let \(x=−δ/2\).
Thus,
\(|x−0|=∣−\frac{δ}{2}−0∣=\frac{δ}{2}<δ\)
and
\(\left|\frac{∣−\frac{δ}{2}∣}{−\frac{δ}{2}}−L\right|=|−1−L|=L+1≥1>\frac{1}{2}=ε\).
On the other hand, if \(L<0\), then let \(x=δ/2\). Thus,
\(|x−0|=∣\frac{δ}{2}−0∣=\frac{δ}{2}<δ\)
and
\(\left|\frac{∣\frac{δ}{2}∣}{\frac{δ}{2}}−L\right|=|1−L|=|L|+1≥1>\frac{1}{2}=ε\).
Thus, for any value of \(L\), \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→0}\frac{|x|}{x}≠L.\)
One-Sided Limits
Just as we first gained an intuitive understanding of limits and then moved on to a more rigorous definition of a limit, we now revisit one-sided limits. To do this, we modify the epsilon-delta definition of a limit to give formal epsilon-delta definitions for limits from the right and left at a point. These definitions only require slight modifications from the definition of the limit. In the definition of the limit from the right, the inequality \(0<x−a<δ\) replaces \(0<|x−a|<δ\), which ensures that we only consider values of \(x\) that are greater than (to the right of) \(a\). Similarly, in the definition of the limit from the left, the inequality \(−δ<x−a<0\) replaces \(0<|x−a|<δ\), which ensures that we only consider values of \(x\) that are less than (to the left of) \(a\).
Definition: One-Sided Limits (Formal)
Limit from the Right: Let \(f(x)\) be defined over an open interval of the form \((a,b)\) where \(a<b\). Then
\[\lim_{x→a^+}f(x)=L\]
if for every \(ε>0\), there exists a \(δ>0\), such that if \(0<x−a<δ\), then \(|f(x)−L|<ε\).
Limit from the Left: Let \(f(x)\) be defined over an open interval of the form \((b,c)\) where \(b<c\). Then,
\[\lim_{x→c^−}f(x)=L\]
if for every \(ε>0\),there exists a \(δ>0\) such that if \( −δ<x−c<0\), then \(|f(x)−L|<ε\).
Example \(\PageIndex{7}\): Proving a Statement about a Limit From the Right
Prove that
\[\lim_{x→4^+}\sqrt{x−4}=0.\nonumber\]
Solution
Let \(ε>0\).
Choose \(δ=ε^2\). Since we ultimately want \(∣\sqrt{x−4}−0∣<ε\), we manipulate this inequality to get \(\sqrt{x−4}<ε\) or, equivalently, \(0<x−4<ε^2\), making \(δ=ε^2\) a clear choice. We may also determine \(δ\) geometrically, as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\).

Assume \(0<x−4<δ\). Thus, \(0<x−4<ε^2\). Hence, \(0<\sqrt{x−4}<ε\). Finally, \(\left|\sqrt{x−4}−0\right|<ε\). Therefore, \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→4^+}\sqrt{x−4}=0\).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Find \(δ\) corresponding to \(ε\) for a proof that \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→1^−}\sqrt{1−x}=0\).
- Hint
-
Sketch the graph and use Example \(\PageIndex{7}\) as a solving guide.
- Answer
-
\(δ=ε^2\)
Infinite Limits
We conclude the process of converting our intuitive ideas of various types of limits to rigorous formal definitions by pursuing a formal definition of infinite limits. To have \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→a}f(x)=+∞\), we want the values of the function \(f(x)\) to get larger and larger as \(x\) approaches a. Instead of the requirement that \(|f(x)−L|<ε\) for arbitrarily small \(ε\) when \(0<|x−a|<δ\) for small enough \(δ\), we want \(f(x)>M\) for arbitrarily large positive \(M\) when \(0<|x−a|<δ\) for small enough \(δ\). Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\) illustrates this idea by showing the value of \(δ\) for successively larger values of \(M\).
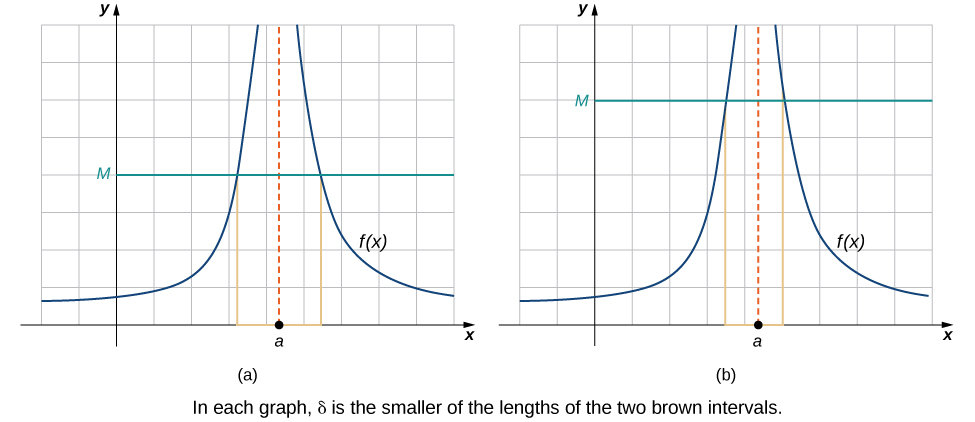
Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\): These graphs plot values of \(δ\) for \(M\) to show that \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→a}f(x)=+∞\).
Definition: Infinite Limits (Formal)
Let \(f(x)\) be defined for all \(x≠a\) in an open interval containing \(a\). Then, we have an infinite limit
\[\lim_{x→a}f(x)=+∞\]
if for every \(M>0\), there exists \(δ>0\) such that if \(0<|x−a|<δ\), then \(f(x)>M\).
Let \(f(x)\) be defined for all \(x≠a\) in an open interval containing \(a\). Then, we have a negative infinite limit
\[\lim_{x→a}f(x)=−∞\]
if for every \(M>0\), there exists \(δ>0\) such that if \(0<|x−a|<δ\), then \(f(x)<−M\).
Example \(\PageIndex{8}\): Proving a Statement about an Infinite Limit
Prove that \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→3}\frac{1}{(x-3)^2}=\infty.\)
Solution
We use a very similar approach to our previous Problem-Solving Strategy. We first find an appropriate \(δ>0\). Then we write our proof.
Step 1: First we find an appropriate \(δ>0\).
1. Let \(M\) be any real number such that \(M>0\).
2. Let \(f(x) = \dfrac{1}{(x-3)^2} > M\). Then we solve for the expression \(x - 3\).
Multiplying both sides of the inequality by the positive quantity \((x - 3)^2\) and dividing both sides by the positive quantity \(M\) gives us:
\[ \frac{1}{M} > (x-3)^2 \nonumber\]
Taking the square root of both sides, we have,
\[ \sqrt{\frac{1}{M}} > |x - 3|. \qquad \quad\left(\text{Remember that }\sqrt{x^2} = |x|.\right)\nonumber\]
Rewriting this statement gives us, \(0 < |x-3| < \sqrt{\dfrac{1}{M}}\). From this we choose \(δ = \sqrt{\dfrac{1}{M}}\).
Step 2: Now we write a proof.
3. Let \(δ = \sqrt{\dfrac{1}{M}}\) and assume \(0 < |x-3| < δ = \sqrt{\dfrac{1}{M}}\).
Thus,
\[ |x-3| < \sqrt{\frac{1}{M}}. \nonumber\]
Squaring both sides gives us,
\[ (x-3)^2 < \frac{1}{M}. \nonumber\]
Taking the reciprocal of both sides (and remembering that this will reverse the direction of the inequality),
\[ \dfrac{1}{(x-3)^2} > M. \nonumber\]
Therefore, we have proven that
\[\lim_{x→3}\frac{1}{(x-3)^2}=\infty.\nonumber\]
A very similar proof will be needed for a limit that is equal to \(-\infty\).
Note that a one-sided limit approach will often need to be taken with this type of limit. For example, to prove: \(\displaystyle \lim_{x\to 0^+}\frac{1}{x} = \infty\).
Key Concepts
- The intuitive notion of a limit may be converted into a rigorous mathematical definition known as the epsilon-delta definition of the limit.
- The epsilon-delta definition may be used to prove statements about limits.
- The epsilon-delta definition of a limit may be modified to define one-sided limits.
- A similar definition of an infinite limit can be used to prove statements about infinite limits.
Glossary
- epsilon-delta definition of the limit
- \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→a}f(x)=L\) if for every \(ε>0\), there exists a \(δ>0\) such that if \(0<|x−a|<δ\), then \(|f(x)−L|<ε\)
- triangle inequality
- If \(a\) and \(b\) are any real numbers, then \(|a+b|≤|a|+|b|\)
- formal definition of an infinite limit
- \(\displaystyle \lim_{x→a}f(x)=\infty\) if for every \(M>0\), there exists a \(δ>0\) such that if \(0<|x−a|<δ\), then \(f(x)>M\)
\(\displaystyle \lim_{x→a}f(x)=-\infty\) if for every \(M>0\), there exists a \(δ>0\) such that if \(0<|x−a|<δ\), then \(f(x)<-M\)
Contributors and Attributions
- Template:ContribOpenStaxCalc
- Paul Seeburger (Monroe Community College), added Example \(\PageIndex{8}\) and entries for infinite limits under Key Concepts and the Glossary.

