4.8: Ternary plots
- Page ID
- 45040
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Introduction
Ternary plots, called de Finetti diagram in population genetics, is used to display three ratio variables that, together, sum to one. For example, display frequency of the three genotypes of a one gene, two allele system in a population.
Download the package Ternary from the R mirror. From the Ternary package, we can get a blank plot by simply calling the function TernaryPlot(). R returns the blank plot to the Graphics window (Fig. \(\PageIndex{1}\)).
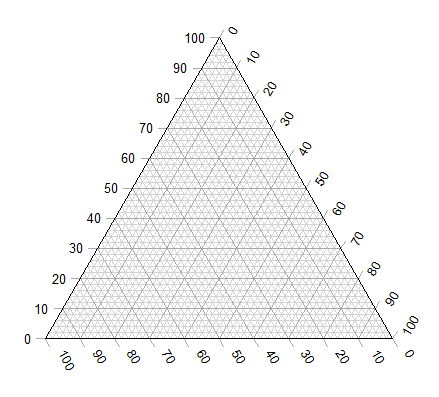
The basic ternary plot is shown in Figure 1. Running from one corner to another you can see how the frequencies range from 0 to 100%. While we can use the Ternary package, other packages allow you to make ternary plots too, including HardyWeinberg. This package includes several useful tests of the Hardy Weinberg model for population genetics data, so we’ll use that package.
Or example will use the HWTernaryPlot function in the HardyWeinberg package. Before proceeding with the example, download and install the package.
A nice site on ternary plots in Microsoft Excel (24 steps!) is provided at chemostratigraphy.com. Instructions also worked for LibreOffice Calc (pers. obs.). Take a look at www.ternaryplot.com for a really nice online plot builder.
Example. Recall your basic population genetics, for a locus with 2 alleles with frequency \(p\) and \(q\) in the population, and given Hardy-Weinberg assumptions apply (e.g., no evolution!), then expected genotype frequencies are given by expanding \((p + q)^{2} = 1\).
Consider a population genetics example using Skittles (Fig. \(\PageIndex{2}\)).

For several bags, count the greens \((p)\) and the oranges \((q)\). Data for 17 mini bags are reported in Table \(\PageIndex{1}\).
| Bag | GREEN | ORANGE |
|---|---|---|
| bag1 | 4 | 2 |
| bag2 | 8 | 2 |
| bag3 | 3 | 3 |
| bag4 | 3 | 4 |
| bag5 | 5 | 7 |
| bag6 | 5 | 1 |
| bag7 | 13 | 5 |
| bag8 | 4 | 2 |
| bag9 | 6 | 3 |
| bag10 | 3 | 2 |
| bag11 | 5 | 4 |
| bag12 | 9 | 9 |
| bag13 | 0 | 2 |
| bag14 | 7 | 3 |
| bag15 | 5 | 4 |
| bag16 | 6 | 2 |
| bag17 | 2 | 3 |
Next, we calculate the genotype frequencies from our counts. For example, for bag1, \(p = 4/6\) and \(q = 2/6\). We can imagine a diploids at the locus: GG, GO, and OO, with frequencies \(p^{2}\), \(2 pq\), and \(q^{2}\). The frequencies for the three genotypes are shown in Table \(\PageIndex{2}\).
| Bag | \(p^{2}\) | \(2pq\) | \(q^{2}\) |
|---|---|---|---|
| bag1 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.11 |
| bag2 | 0.64 | 0.32 | 0.04 |
| bag3 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.25 |
| bag4 | 0.18 | 0.49 | 0.33 |
| bag5 | 0.17 | 0.49 | 0.34 |
| bag6 | 0.69 | 0.28 | 0.03 |
| bag7 | 0.52 | 0.40 | 0.08 |
| bag8 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.11 |
| bag9 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.11 |
| bag10 | 0.36 | 0.48 | 0.16 |
| bag11 | 0.31 | 0.49 | 0.20 |
| bag12 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.25 |
| bag13 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| bag14 | 0.49 | 0.42 | 0.09 |
| bag15 | 0.31 | 0.49 | 0.20 |
| bag16 | 0.56 | 0.38 | 0.06 |
| bag17 | 0.16 | 0.48 | 0.36 |
For the plot, the HWTernaryPlot function expects counts, not frequencies of three genotypes of a gene in a population, with genotype frequency that sums to one. Table 3 shows calculated genotype data, assuming 20 Skittle diploid critters per bag.
| Bag | GG | GO | OO |
|---|---|---|---|
| bag1 | 9 | 9 | 2 |
| bag2 | 13 | 6 | 1 |
| bag3 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| bag4 | 4 | 10 | 7 |
| bag5 | 3 | 10 | 7 |
| bag6 | 14 | 6 | 1 |
| bag7 | 10 | 8 | 2 |
| bag8 | 9 | 9 | 2 |
| bag9 | 9 | 9 | 2 |
| bag10 | 7 | 10 | 3 |
| bag11 | 6 | 10 | 4 |
| bag12 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| bag13 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| bag14 | 10 | 8 | 2 |
| bag15 | 6 | 10 | 4 |
| bag16 | 11 | 8 | 1 |
| bag17 | 3 | 10 | 7 |
Example
Create an R data.frame called skittles from Table \(\PageIndex{3}\). Because HWTernaryPlot requires input only of the genotype data, remove the first column
dSkittles <- subset(skittles, select = -c(Bag) )
require(HardyWeinberg)
#Create a Ternaryplot
HWTernaryPlot(dLactose,100,pch=19, cex=2, region=1,hwcurve=TRUE, curvecols=c("red", "green"), vbounds=FALSE, vertex.cex=2, verbose=TRUE)
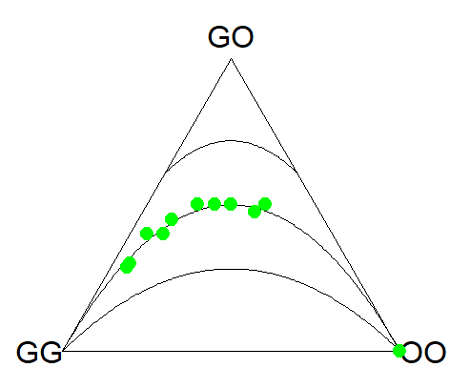
What do we have? The function plots three convex curved lines. The green points are the heterozygote (GO) frequencies. They all fall on the middle line, as expected, because I had used HW to calculate frequency of the heterozygotes. If any population had numbers of observed heterozygotes different from expected values, then the population point would be represented by a red point and it would fall in one of the regions above or below the curved lines.
Question
- Repeat the Skittles example, but replace with counts for purple (p) and red (q) candies (scroll down to data below, or click here).
- Optional: A more realistic example would be to draw 2 candies from Skittles bag and record the counts (e,g, how many purple+purple, purple+red, red+red pairs drawn), then make Ternary plots on the observed and not the expected frequencies.
- Genetic example. The ternary plot is useful for displaying population genetic frequency data. For example, ability to digest lactose, i.e., lactase persistence, is in part due to genotype at SNP rs4988235 (Enattah et al 2002). Genotypes CC tend to be lactose intolerant, genotypes CT and TT are lactose tolerant. I gathered allele frequencies from the ALFRED database for several human populations, calculated genotype frequencies assuming Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. I also created results for a hypothetical population “Madeup.” (Scroll down to data below, or click here). Enter the data into R as a dataframe, e.g.,
data.SNP, copy R code from this page, make the necessary changes, and recreate the plot shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\).- What do you conclude about the heterozygotes in Madeup population?

Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\): rs4988235 genotype frequencies, data.SNP.
- What do you conclude about the heterozygotes in Madeup population?
- Add a new row of data to your rs4988235 data set,
data.SNP. CC= 4, CT = 10, TT = 6. The data were derived from frequencies reported in Figure 2, Baffour-Awuah et al 2016 (PMC4308731). To add a new row, modify the code belowdata.SNP <- rbind(data.SNP, “PMC4308731” = c(4, 10, 6))
Create another ternary plot, and address whether or not this new data set shows heterozygotes in agreement with Hardy Weinberg assumptions.
Data sets
Skittles Data
| Bag | PURPLE | RED |
|---|---|---|
| bag1 | 3 | 3 |
| bag2 | 8 | 4 |
| bag3 | 2 | 4 |
| bag4 | 2 | 1 |
| bag5 | 7 | 6 |
| bag6 | 3 | 2 |
| bag7 | 5 | 5 |
| bag8 | 2 | 5 |
| bag9 | 4 | 4 |
| bag10 | 3 | 5 |
| bag11 | 3 | 2 |
| bag12 | 8 | 6 |
| bag13 | 2 | 5 |
| bag14 | 7 | 6 |
| bag15 | 3 | 1 |
| bag16 | 2 | 4 |
| bag17 | 4 | 1 |
SNP Data
| Population | C | CT | T |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mambila | 99 | 1 | 0 |
| Ben Amir | 99 | 1 | 0 |
| Zaramo | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| Bedouin | 95 | 5 | 0 |
| Druze | 93 | 7 | 0 |
| Kuwaiti | 86 | 13 | 1 |
| Dutch | 12 | 45 | 43 |
| Finns | 3 | 29 | 68 |
| Swedes | 1 | 13 | 87 |
| Bengali | 87 | 13 | 1 |
| Naga | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| Mala | 88 | 12 | 0 |
| Han | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| Japanese | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| Koreans | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| Cheyene | 93 | 7 | 0 |
| Pima | 98 | 2 | 0 |
| Maya | 90 | 10 | 0 |
| Brazilian | 50 | 42 | 9 |
| Chilean | 60 | 35 | 5 |
| Colombian | 81 | 18 | 1 |
| Madeup | 40 | 5 | 55 |


