15.2.5: Chapter 6 Homework
- Page ID
- 28308
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)\(\newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
- Explain the difference between population parameters and sample statistics. What symbols do we use for the mean and standard deviation for each of these?
- Consider the following probability distribution function of the random variable X, which represents the number of people in a group(party) at a restaurant:
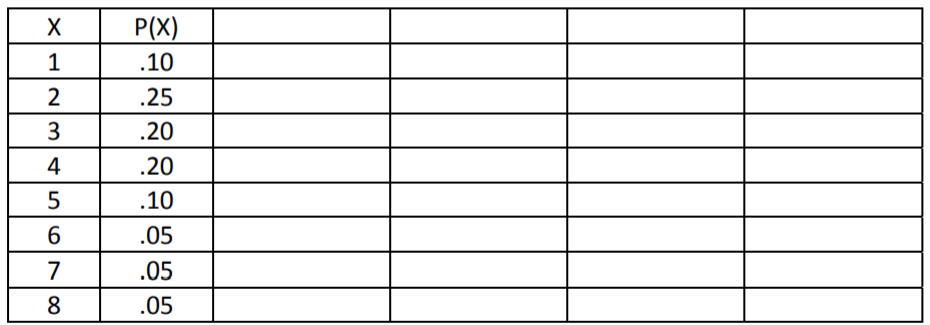
- Find the population mean of X.
- Find the population variance and standard deviation of X.
- Find the probability that the next party will be over 4 people.
- Find the probability that the next three parties (assuming independence) will each be over 4 people.
- 10% of all children at a large urban elementary school district have been diagnosed with learning disabilities. 10 children are randomly and independently selected from this school district.
- Let X = the number of children with learning disabilities in the sample. What type of random variable is this?
- Find the mean and standard deviation of X.
- Find the probability that exactly 2 of these selected children have a learning disability.
- Find the probability that at least 1 of these children has a learning disability.
- Find the probability that fewer than 3 of these children have a learning disability.
- A general statement is made that an error occurs in 10% of all retail transactions. We wish to evaluate the truthfulness of this figure for a particular retail store, say store A. Twenty transactions of this store are randomly obtained. Assuming that the 10% figure also applies to store A, and let X be the number of retail transactions with errors in the sample
- The probability distribution function (pdf) of X is binomial. Identify the parameters n and p.
- Calculate the expected value of X.
- Calculate the variance of X.
- Find the probability exactly 2 transactions sampled are in error.
- Find the probability at least 2 transactions sampled are in error.
- Find the probability that no more than one transaction is in error.
- Would it be unusual if 5 or more transactions were in error?
- A newspaper finds a mean of 4 typographical errors per page. Assume the errors follow a Poisson distribution.
- Let X equal the number of errors on one page. Find the mean and standard deviation of this random variable.
- Find the probability that exactly three errors are found on one page.
- Find the probability that no more than 2 errors are found on one page.
- Find the probability that no more than 2 errors are found on two pages.
- Major accidents at a regional refinery occur on the average once every five years. Assume the accidents follow a Poisson distribution.
- How many accidents would you expect over 10 years?
- Find the probability of no accidents in the next 10 years.
- Find the probability of no accidents in the next 20 years.
- 20% of the people in a California town consider themselves vegetarians. If 20 people are randomly sampled, find the probability that:
- Exactly 3 are vegetarians.
- At least 3 are vegetarians.
- At most 3 are vegetarians
- 20% of the people in a California town consider themselves vegetarians. People are sampled until the first vegetarian is found. Use the geometric distribution to find the following probabilities:
- A vegetarian is picked on the first trial.
- A vegetarian is picked somewhere within the first three trials.
- A vegetarian is not picked until sometime after the third trial.
- Cargo ships arrive at a loading dock at a rate of 2 per day. The dock has the capability of handling 3 arrivals per day. How many days per month (assume 30 days in a month) would you expect the dock to be unable to handle all arriving ships? (Hint: first find the probability that more than 3 ships arrive, and then use that probability to find the expected number of days in a month that too many ships arrive).
- Major hurricanes strike the U.S. coast at a rate of 0.7 per year.
- What is the probability that 4 major hurricanes strike the U.S. coast in one year?
- What is the probability that more than 2 major hurricanes strike the U.S. coast in 2 years?
- What is the probability that no major hurricane will strike the U.S. coast in the next 5 years?
- In 2017, 3 major hurricanes made landfall in the United States, causing catastrophic damage to Texas, Florida, Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands. Find the probability of three major hurricanes making landfall in one year.


